Canine Meibomian Gland Tumors
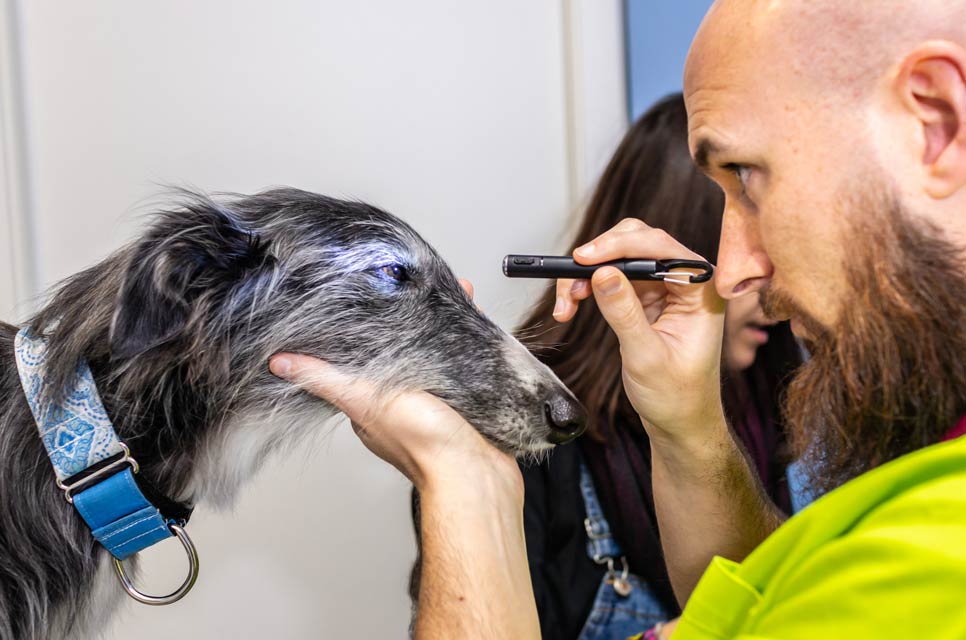
Meibomian gland tumors occur in a dog's eyelids. They're quite common, especially in older dogs.
What Causes Meibomian Gland Tumors in Dogs?
The Meibomian glands provide the eyes with oily moisture that keeps the tear film on the cornea stable. They are sebaceous glands, which are also found in other areas of the skin.
Tumors in the Meibomian glands result in bumps along the inside or edges of the eyelids. They may pop outward or turn inward and rub on the cornea.
Meibomian gland tumors in dogs are usually benign (non-cancerous), so they don't typically spread or move to other areas of the body.
Canine meibomian gland tumors can become irritated, painful, and even infected, or they can cause corneal ulcers or conjunctivitis.
In dogs, Meibomian gland tumors usually grow slowly.
Signs of Meibomian Gland Tumors in Dogs
The tumor is visible along an edge of the eyelid as a firm bump. The eye may have excessive tearing, and if the tumor is rubbing on the cornea, the dog may paw at the eye or rub his head on items.
Treatment of Meibomian Gland Tumors in Dogs
Meibomian gland tumors must be removed surgically. It can be done with a blade or cryosurgery (freezing). Removal requires general anesthesia for the dog. If the tumor is very large, the result may be a slightly deformed eyelid.
After surgery, the dog must not be allowed to rub their face on the ground or paw at it, so an E-collar will most likely be necessary. Eye drops for inflammation and antibiotics may be prescribed.
If the eye itself has secondary issues like corneal ulcer or conjunctivitis, that will need to be treated after surgery as well.
You May Also Like These Articles:
Disclaimer: This website is not intended to replace professional consultation, diagnosis, or treatment by a licensed veterinarian. If you require any veterinary related advice, contact your veterinarian promptly. Information at DogHealth.com is exclusively of a general reference nature. Do not disregard veterinary advice or delay treatment as a result of accessing information at this site. Just Answer is an external service not affiliated with DogHealth.com.
Notice: Ask-a-Vet is an affiliated service for those who wish to speak with a veterinary professional about their pet's specific condition. Initially, a bot will ask questions to determine the general nature of your concern. Then, you will be transferred to a human. There is a charge for the service if you choose to connect to a veterinarian. Ask-a-Vet is not manned by the staff or owners of DogHealth.com, and the advice given should not delay or replace a visit to your veterinarian.


